Amino acids(AAs) are nutrients primarily responsible for protein synthesis. They play a crucial role in almost all tissues and participate in various metabolic pathways, even in small quantities (NASEM, 2021).

Supplementation of dairy cow diets with essential amino acids aims to meet needs and improve the amino acid balance when protein sources in the diet are insufficient. Effects on milk production, milk protein synthesis (BRAKE et al., 2013), cow weight gain, and immune response have been observed with supplementation (ABREU et al., 2023).
Among the essential amino acids that need to be supplemented in ruminants, lysine and methionine are the most restrictive and thus provide greater productive benefits with supplementation (SCHWAB; BRODERICK, 2017).
In this context, this article aims to summarize the main aspects of amino acid supplementation in the nutrition of dairy cattle.
PROTEINS
These are the main nitrogenous compounds present in the feeds offered in ruminant diets, varying in concentration levels and ruminal degradation. According to the National Research Council (NRC, 2001), proteins are macromolecules that differ in size, types, structure, and functions. They are composed of building units, amino acids, which are linked by peptide bonds and can be defined in Nitrogen X 6.25, amounting to 16g of nitrogen in 100g of true protein.
Protein can be divided into two fractions:
a) rumen-degradable protein (RDP) and
b) rumen-undegradable protein (RUP)
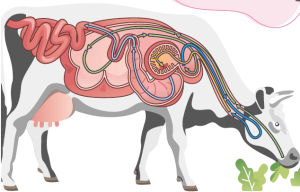
 The degradation of CP occurs through the action of enzymes (proteases, peptidases, and deaminases) secreted by ruminal bacteria, which degrade the RDP fraction of CP into amino acids, peptides, and ammonia for their own consumption, such as microbial protein synthesis and cell multiplication (NRC 1996; NRC, 2001).
The degradation of CP occurs through the action of enzymes (proteases, peptidases, and deaminases) secreted by ruminal bacteria, which degrade the RDP fraction of CP into amino acids, peptides, and ammonia for their own consumption, such as microbial protein synthesis and cell multiplication (NRC 1996; NRC, 2001).
RUMEN DEGRADABLE PROTEIN (RDP)
It is the fraction of CP utilized by the consumption of microorganisms in the rumen. In this degradation process, RDP undergoes the action of various enzymes secreted by ruminal microorganisms, including proteases, peptidases, and deaminases, which use amino acids, peptides, and ammonia to carry out the process of cell multiplication to synthesize MicP (MABJEESH et al., 1997; MARINO, 2015).
RUMEN UNDEGRADABLE PROTEIN (RUP)
Also known as “bypass” protein, is the fraction of protein that “escapes” ruminal degradation, either due to low degradability of the feed or because it has undergone some form of treatment (MCDONALD et al., 2012).
The flow of RUP is determined by the combination of passage and degradation rate of CP reaching the rumen. Amino acids reaching the intestine as metabolized protein are determined by both the flow of feed protein that “escapes” the rumen as RUP and MicP, endogenous protein from the cow itself, and the amino acid composition of these proteins (ZANTON, 2017).
MicP can be considered the main source of Metabolizable Protein (MP) in the intestines of ruminants, reaching levels of 45 to 55% of MP in high-producing dairy cows; it can be controlled by the amount of organic matter fermented in the rumen, and its quality can be estimated by the essential amino acid profile (SANTOS et al., 1998).
The requirement for MP is met by the absorption in the small intestine of true MicP and RUP. For beef cattle, MicP can supply 50 to 100% of the MP requirements due to its high digestibility and amino acid profile (NRC, 2001).
An increase in RUP does not guarantee better performance, especially when there is a decrease in levels of MicP for the duodenum, as essential nutrients for cows, amino acids, are provided by the digestion of MicP and true dietary protein that is not metabolized in the rumen, as RUP can provide a considerable fraction of the required amino acids, but this fraction does not exceed 50% (SANTOS et al., 1998; SCHWAB; BRODERICK, 2017).

AMINO ACIDS
Amino acids are structural units of proteins, possessing genetic code information to meet the organism’s requirements. However, only 20 are genetically coded. They are compounds characterized by a group of amino (-NH3) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) in their molecules, with the exception of proline, which contains an amino group (-NH-) instead of an amino group.
In ruminant nutrition, essential amino acids are considered those supplied endogenously, and non-essential amino acids are supplied exogenously.
- Non-essential amino acids are synthesized endogenously by animal tissue from intermediate metabolism metabolites and amino acid groups. They can be synthesized from other non-essential amino acids or, when necessary, from essential AAs.
Examples include: alanine, aspartic acid, asparagine, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
- Essential amino acids are not produced by the organism, and if they are (arginine and histidine), it is in small quantities.
Examples include: histidine, arginine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
For the use of amino acids in diets, it is necessary to consider that:
- the efficiency of amino acids is not constant.
- it is necessary to meet protein maintenance demands before satisfying the production requirements in dairy cows.
- the stage of lactation also plays a significant role in determining the use of amino acids.
- it is essential to provide cows with adequate amounts of amino acids to optimize their health, reproduction, and milk production (GALINDO et al., 2015).
Amino acid absorption occurs through three main pathways:

(SCHWAB; WHITEHOUSE, 2021).
MicP usually accounts for over 50% of the flow of crude protein (CP) to the small intestine (SCHWAB; BRODERICK, 2017) and is obtained through the use of dietary nitrogen, provided by rumen-degradable protein (RDP).
While MicP represent the majority of the AA supply for dairy cows, to adequately meet amino acid needs in dairy cow diets, a proper balance between RDP and PDNR sources must be considered, especially for dairy production where supplementation with synthetic amino acids may be another choice.
DIGESTION AND METABOLISM OF PROTEIN AND AMINO ACIDS IN THE RUMEN
The degradability process can be characterized by the conversion of dietary protein into ammonia, involving the processes of protein digestion into amino acids and the fermentation process of amino acids into fatty acids (RUSSELI et al., 1992).
The amount of AAs provided in diets must meet the needs, thus fulfilling maintenance requirements. When the animal is placed in an environment that demands high performance, the scenario changes, as these requirements tend to increase. It is necessary to achieve maximum efficiency in microbial protein synthesis and ensure that the dietary protein portion is not degraded in the ruminal environment (BRODERICK; MERCHEN, 1992; TORRES, 2015).
The utilization of protein and the degradation processes of proteins occur through their hydrolysis carried out by enzymes secreted by ruminal proteolytic microorganisms, transforming them into peptides and amino acids. The released amino acids are absorbed by microbial protein or can be converted into ammonia and carbon skeletons (CHALUPA, 1975). In other words, protein degradation occurs thanks to a multi-enzymatic system associated with the cell membranes of ruminal bacteria (KOZLOSKI, 2017).
Microbial protein reaches the animal’s intestine, along with RUP, and serves as a source of AAs for maintenance, growth, and milk production.
It can be found that 50 to 90% of microbial protein passes into the duodenum (SANTOS, 2006).
Extracellular degradation begins with the hydrolysis of protein molecules, resulting in oligopeptides. Subsequently, oligopeptides undergo the hydrolysis process, transforming into aminopeptidases, releasing dipeptides, and dipeptides undergo another hydrolysis process, releasing AAs. The amino acids and peptides resulting from the hydrolysis process are subsequently taken up by ruminal bacteria (MCDONALD et al., 2012). Amino acids can subsequently be incorporated into microbial protein or be deaminated and metabolized, releasing ammonia and forming alpha-keto acids that will later be converted into volatile fatty acids (VFA) (KOZLOSKI, 2017).
(Figure 1)
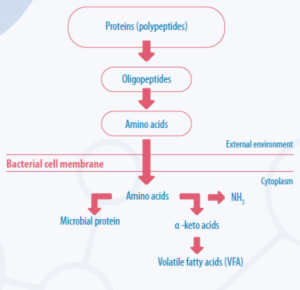
All protein degradation upon reaching the rumen is carried out by ruminal bacteria, with the majority being cellular on the surface, and only 10% of degradation is attributed to free bacteria in the rumen (Figure 2) (KOZLOSKI, 2017).
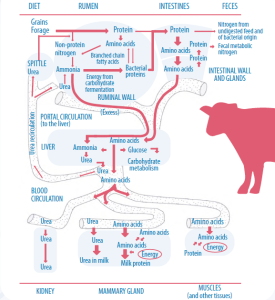
Figure 2 Protein metabolism in dairy cattle. Source (Wattiaux, 2002)
You may also like to read: “Boosting Metabolic Efficiency in Dairy Cows through Folic Acid and Vitamin B12″