 15 Dec 2022
15 Dec 2022
![]() Phosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient for livestock, but its utilization efficiency is less than 40%, contributing to environmental problems.
Phosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient for livestock, but its utilization efficiency is less than 40%, contributing to environmental problems.
In this review, we summarize recent approaches to optimize the availability of P in livestock diets and improve their utilization efficiency.

It has been proven that phased feeding manages to reduce P excretion by 20%. The addition of phytase enzymes to diets increased P availability from 42% to 95%. Low-phytate transgenic plants and transgenic animals increased phosphorus availability by 14% and 52–99%, respectively (Brask-Pedersen et al., 2011).
![]()
In practice, a combination of phased feeding and enzyme addition has the greatest potential for P reduction.
On the other hand, functional and nutritional genomics can provide tools to improve efficiency in the future. Phosphorus reserves are finite. Therefore, losses not only cause environmental damage but also represent the waste of a depleted resource. [register]
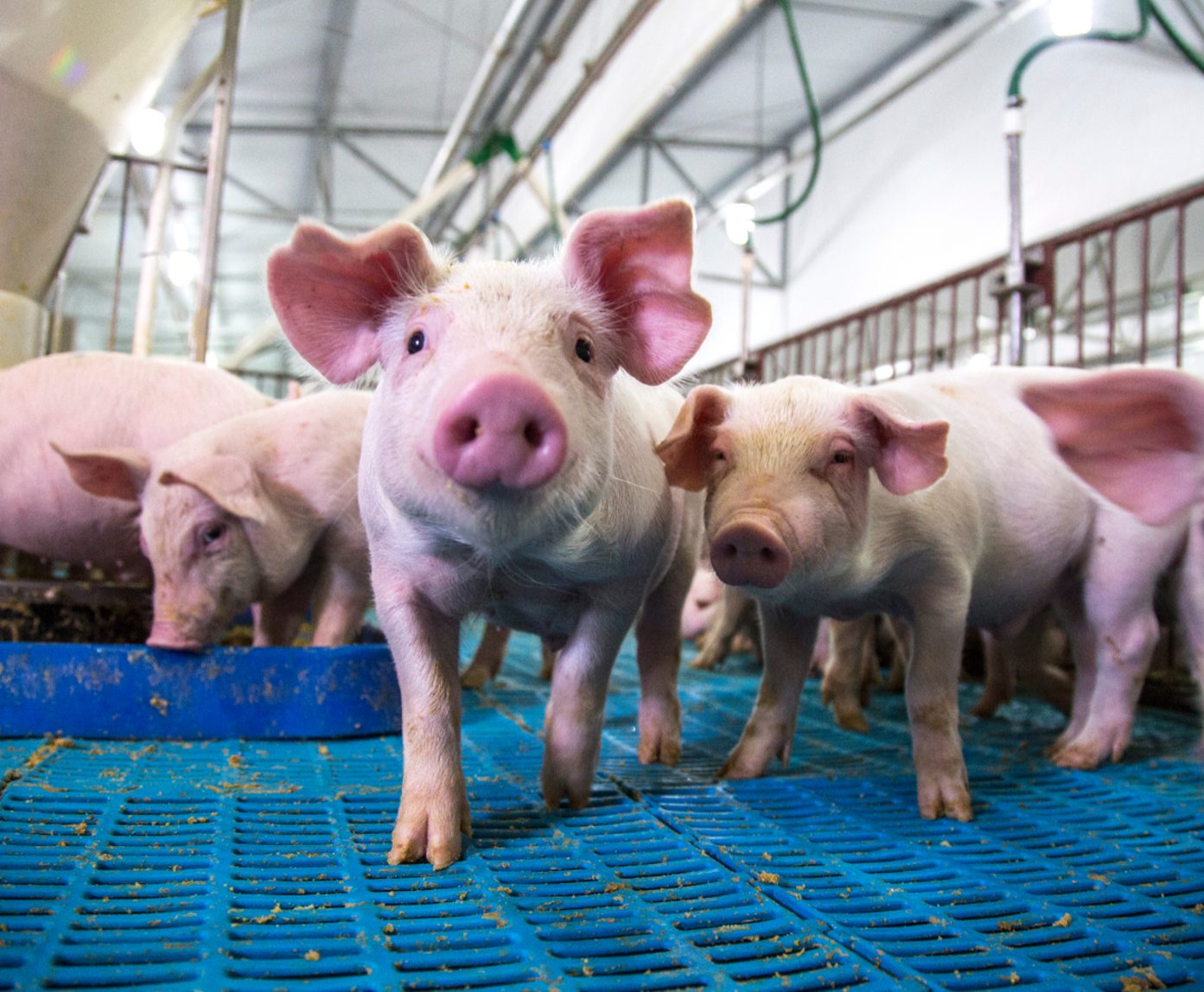
![]() In the United States, the livestock sector is responsible for approximately 33% of the phosphorus load in freshwater resources (Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 1998).
In the United States, the livestock sector is responsible for approximately 33% of the phosphorus load in freshwater resources (Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 1998).

Phosphorus is an essential macromineral for all animals, which must be supplied in sufficient quantities as it plays an important role in bone development, growth and the productivity of livestock.
The need to use inorganic P in livestock diets has to do with the fact that the organic P present in some feeds, may not always be completely available for absorption by the animals. (Zhang et al., 200).
![]() Cattle excrete a large amount of P as less than 40% of consumed P is generally absorbed. This depends on:
Cattle excrete a large amount of P as less than 40% of consumed P is generally absorbed. This depends on:
There are current opportunities available to help reduce excess P excretion from livestock. These can be divided into two categories:
![]() Improving or optimizing P availability in feed
Improving or optimizing P availability in feed
![]() Increasing livestock efficiency through greater incorporation of P into the product or through faster growth rates
Increasing livestock efficiency through greater incorporation of P into the product or through faster growth rates
Matching P requirements of animals with the available P in diets through accurate predictions, feed formulation methods, and feeding animals in groups according to their physiological state, are all tools that contribute to significantly reduce phosphorus excretion.

 Phosphorus availability can also be substantially improved in monogastric animals through the use of enzymes such as phytases which break down organic P.
Phosphorus availability can also be substantially improved in monogastric animals through the use of enzymes such as phytases which break down organic P.
Cattle can increase their efficiency in P-utilization by incorporating genes that control the production of enzymes which help break down organically bound P and make it available for the animal (Johansen et al., 2003).
![]() Functional and nutritional genomics are new areas of study that will help us understand how animals interact with their environment and how they are able to respond to nutritional demands by matching P demand with dietary supply more accurately.
Functional and nutritional genomics are new areas of study that will help us understand how animals interact with their environment and how they are able to respond to nutritional demands by matching P demand with dietary supply more accurately.
Diet formulation strategies to avoid excess phosphorus
Formulating a complete feed in livestock production systems involves determining a combination of ingredients that meets specific nutrient requirements for a target level of production.
Therefore, in a lower cost diet, phosphorus utilization can be optimized through phased feeding. Phased feeding is based on the premise that the population’s P requirements(as well as other essential nutrients) change during growth, lactation and gestation stages.
This reality can be leveraged by feeding multiple diets where each of the diets provides optimal nutrient densities at the midpoint of each subinterval (phase).
![]() A recent evaluation of the concept of phased feeding in growing pigs, covering the growth period of 20 to 120 kg of body weight, has shown a reduction of 20%.
A recent evaluation of the concept of phased feeding in growing pigs, covering the growth period of 20 to 120 kg of body weight, has shown a reduction of 20%.
Precision feeding with individualized requirements
Although phased feeding provides significant improvements in nutrient and phosphorus utilization, diets are still formulated to meet the requirements of a group of animals.
Use of enzymes in animal feed
Plants used as animal feed mainly store their P as phytate (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate, which is poorly available to monogastric animals.
Phytase belongs to a class of phosphatases that allow the dephosphorylation of phytate within the animal’s digestive tract or in feed before its intake.
Genetic manipulation of diets
Food supply in liquid form is predominantly practiced in Northern Europe and may be a potential tool to optimize the utilization of P.
![]()
The use of fermented liquid feed or soaking dry feed for pigs is a method of pre-digesting phytate before feeding.
When food is mixed with water, phytate is subjected to degradation by microbial or plant phytases. The degree of phytate degradation depends on the concentration of phytase within the plant, its addition and the type of microorganisms that are present.
Transgenic animals, functional, and nutritional genomics
A transgenic pig which produced a salivary phytase (E. coli phytase) was developed in Canada during 2001, with the aim of increasing P utilization and minimizing its excretion.
Conclusions
It is believed that optimizing the availability of phosphorus in feed and improving the efficiency of P utilization in livestock will reduce the excretion of this mineral into the environment and help preserve a finite resource.
The formulation of diets should take into account the individual requirements of animals, or at least one group of animals, according to their stage of growth and level of production.
[/register]
Subscribe now to the technical magazine of animal nutrition
AUTHORS

Nutritional Interventions to Improve Fertility in Male Broiler Breeders
Edgar Oviedo
The Use of Organic Acids in Poultry: A Natural Path to Health and Productivity
M. Naeem
Synergistic Benefits of Prebiotics and Probiotics in Poultry, Swine, and Cattle
Gustavo Adolfo Quintana-Ospina
Hybrid Rye Potential in Laying Hen Feed Rations
Gwendolyn Jones
A day in the life of phosphorus in pigs: Part I
Rafael Duran Giménez-Rico
Use of enzymes in diets for ruminants
Braulio de la Calle Campos
Minerals and Hoof Health in the Pregnant Sow
Juan Gabriel Espino
Impact of Oxidized Fats on Swine Reproduction and Offspring
Maria Alejandra Perez Alvarado