Thermal processing of soybean meal for poultry nutrition, Understanding its importance.
Possessing adequate knowledge about the nutritional value of ingredients is a key point when it comes to the formulation of monogastric animal diets. Soybean meal is the main protein source with the highest intake levels within this type of diets. In this regard, Rostagno et al. (2017) recommend up to 35% inclusion of the ingredient in broiler formulations. Therefore, quality control of this raw material is essential for ensuring good animal performance levels in the field.

Raw soybeans contain several anti-nutritional factors, such as protease inhibitors and lectins, as well as allergenic factors such as glycinin and beta conglycinin. These are inactivated through heat treatment during processing. On the other hand, there are other heat-resistant compounds such as: oligosaccharides, non-starch polysaccharides and phytate. (Medic et al., 2014).
Analytical methods to evaluate soybean meal quality
Currently the industry employs two techniques to assess if the grain’s thermal processing has been adequate. These two techniques have become widely adopted as they are easy to execute and hold low laboratory costs. These two tests are known as: solubility in KOH 0.02% and the urease activity test.
Solubility in KOH
Solubility in KOH evaluates the quality of processing and inactivation of anti-nutritional factors. Values above 75% of protein solubility indicate a higher biological quality of protein and better amino acid utilization by the gastrointestinal tract.
When values are below the desirable levels, this indicates that there has been thermal super processing. Causing protein denaturation reactions, complexation of amino acids and a reduction of sugars (Maillard reaction). Consequently, the product loses nutritional quality due to a lower availability of amino acids (Heidenreich, 2000).
Urease activity test
The urease activity test or index is an indirect measuring tool, that indicates if there has been thermal subprocessing through the determination of pH variations.
The higher the value recorded in the test, the greater the urease activity present in the sample.
Raw soybeans should present pH variations that range from 2.0 and 2.5 (Butolo, 2002). After thermal processing toasted soybean meal should have a pH variation within a 0.05 and 0.25 range, according to mapa (1993).
Anti-nutritional factors that impact performance and productivity
Bowman-Birk Factor and Kunitz Factor
The two compounds, Bowman-Birk factor (BBK) and Kunitz factor (KTI), are inhibitors of the activity of proteolytic enzymes formed by amino acids (Liu, 1997).
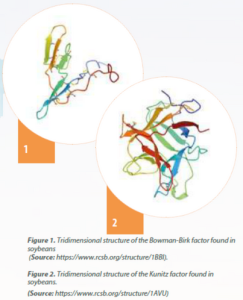
The BBK factor has a variable molecular weight between 6 and 10 KDa and has a structure formed by 71 amino acid residues (Figure 1). Meanwhile the KTI factor has a molecular weight of 20 KDa and is formed by 181 amino acid residues (Figure 2). Both of these are deactivated when soybean meal undergoes correct thermal processing.
Approximately 6% of soybean protein is represented by protease inhibitors (Liu, 1997). When these anti-nutritional factors are present in soybean meal, they can negatively impact bird performance.
The main proteolytic enzymes which are produced in the pancreas are: trypsin and chymotrypsin. Both are endopeptidases that act by breaking non-terminal and specific connections. Trypsin acts on hydrolysis between lysine-arginine and chymotrypsin in hydrolysis among phenylalanine-tyrosine (Rutz, 2002).
Due to the complexation which occurs between proteolytic enzymes and BBK & KTI factors, the pancreas is stimulated to increase its enzymatic secretion in order to compensate for the lack of active trypsin and chymotrypsin. Leading to the presence of free ingested substrates that arrive at the duodenum to be metabolized.

As a consequence of this metabolic imbalance, the digestibility of nutrients contained within the diet is reduced. Triggering a physiological response with hyperplasia and pancreatic hypertrophy (Cabrera-Orozco et al., 2013).
Rocha et al. (2014) demonstrated an increase in the size and number of exocrine cells through the histological examination of pancreatic tissue in broilers fed raw soybean meal (Figure 3).
The inclusion of 12% raw soybean meal can lead to a significant increase of up to 62% in the weight of the pancreas (Rada et al., 2017).
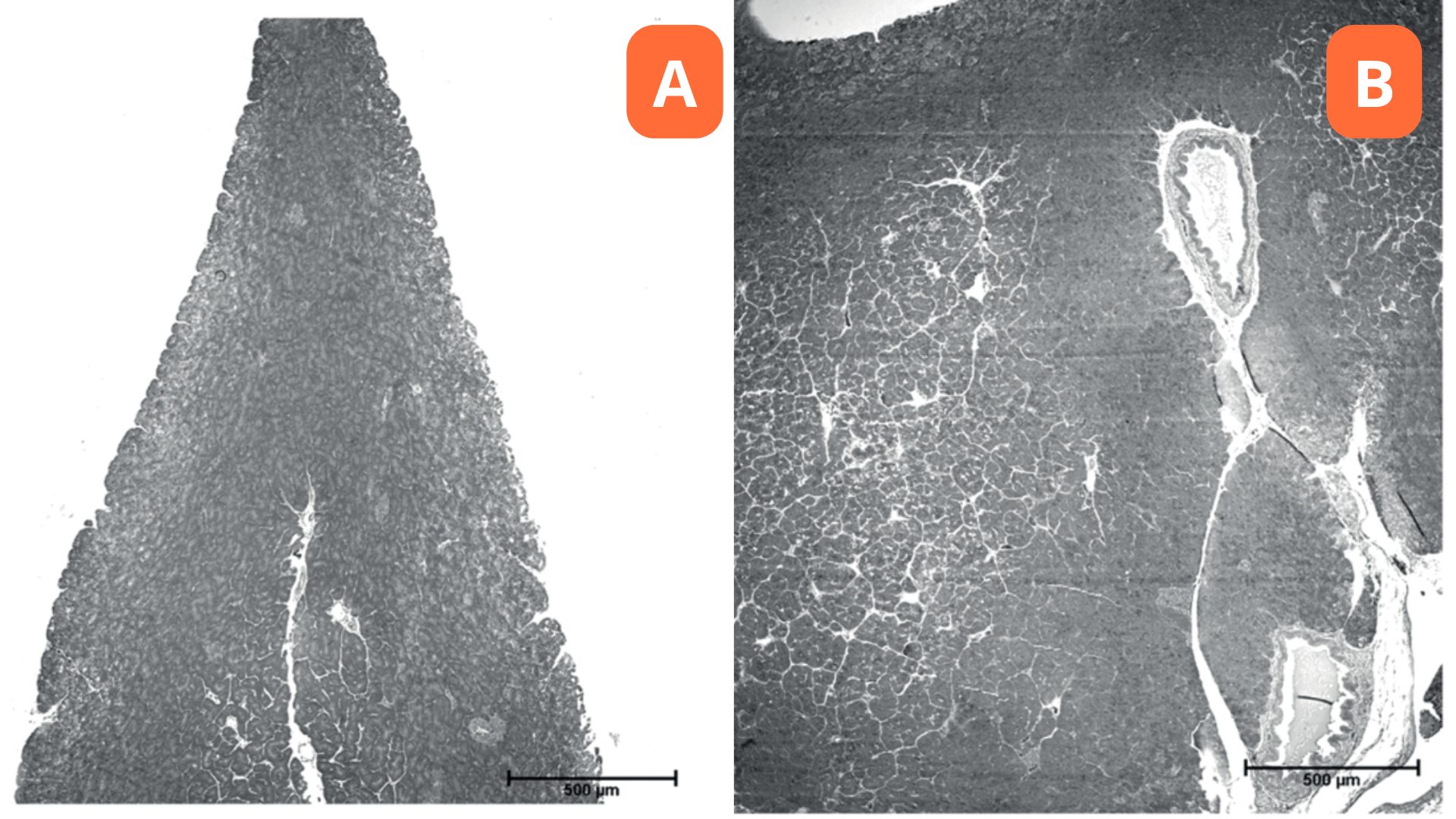
Figure 3. Normal pancreatic parenchyma of broilers fed a control diet (A). Increase in the number and size of pancreatic cells of broilers fed 15% raw soybean (B). (Source: Rocha et al., 2014)
De Coca-Sinova, et al. (2008) analyzed the apparent ileal digestibility of nutrients in broilers that received different soybean meals, and found that the digestibility of nitrogen, crude energy and amino acids was higher when soybean meal was offered with less anti-nutritional factors in its composition.
This demonstrates the importance of the quality of thermal processing for the deactivation of these factors that impair adequate nutrient use in animal diets.
Another heat-sensitive anti-nutritional factor is lectin, or soy hemagglutinin. Its main effects on broilers are: intestinal epithelium damage, decreased villi height, alterations in the activity of brush edge enzymes and hypersecretion of endogenous proteins inducing goblet cell hyperplasia. As a result of the latter, there is an increase in mucus production and a reduction in nutrient absorption from the diet (Grant, 1989; Liener, 1994).
Soy lectin can negatively affect the intestine and immune system of the mucosa by:
- Altering the structure of intestinal cells;
- Increased intestinal permeability due to damage in junction proteins;
- Decreasing the immune response and blocking IgA production;
- Altering the composition of the intestinal microbiota (Pan et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2011).
These implications can significantly reduce the use of nutrients in the diet and cause deleterious effects on animal performance.
The main oligosaccharides found in soybean meal that interfere with broiler metabolism are: stachyose and raffinose. When consumed, these are not hydrolyzed and instead they become fermented within the gastrointestinal tract.
Conventional soybean meal contains approximately 4.61% of stachyose and 0.93% of raffinose in its composition. On the other hand, soybean meal derived from a modified cultivar presents 1.38% and 0.18% of stachyose and raffinose content, respectively (Baker et al., 2011).

In a study comparing soybean meal from modified and conventional cultivars, Parsons et al. (2000) found that there was a 7% increase in metabolizable energy values of the diet of birds that received conventional meal (2,739 Kcal/Kg dM) in relation to those that received a modified meal with low oligosaccharide content (2,931 Kcal/Kg dM).
In addition, the profile and concentration of essential amino acids (lysine, methionine and tryptophan) in soybean meal from modified cultivars with low oligosaccharide content was also altered (Baker et al., 2011). The same authors state that it is possible to reduce the amount of modified soybean meal (32.60%) in the diet compared to conventional meal (38.21%), due to the amino acid composition.
Future prospects
The nutritive value of soybean meal is directly related to the quality of the processing to which the grain is subjected to. When the processing is performed properly, the grain presents high crude protein content (46% to 50%),a good amino acid composition and anti-nutritional factors are correctly deactivated (Swick, 2009).
The ideal soybean meal should present high protein solubility (above 80%) and low urease (below 0.15). As these are indicative of adequate thermal processing and of a product with good nutritional quality.

Quality control of raw materials that reach feed plants is an important step that will directly impact the productivity of monogastric animals. Therefore,adequate knowledge regarding laboratory methodology as well as a proper understanding of the negative impacts caused by the presence of anti-nutritional factors in dietary ingredients, is key .
Source: This article was originally published as a portuguese content in Nutrinews Brasil 4th Trimester 2022