|
Mycotoxins represent a significant challenge to animal production, with their prevalence in raw materials or feeds subject to variations related to changes in climatic conditions. For example, droughts or years with high rainfall affect the types of fungi that proliferate in certain regions (Moretti et al. 2019) |
There are different methods to control the impact of mycotoxins on animal production, ranging from monitoring their presence in raw materials during pre-harvest and post-harvest stages to detoxifying animals exposed to them through contaminated diets
The use of mycotoxin adsorbents is widely recognized as an effective strategy to mitigate the effects of mycotoxins in contaminated animals (Galvano et al., 2001).
![]() Mycotoxin adsorbents are active in the gastrointestinal tract of animals, with mycotoxins binding to the adsorbent matrix through various physico-chemical interactions.
Mycotoxin adsorbents are active in the gastrointestinal tract of animals, with mycotoxins binding to the adsorbent matrix through various physico-chemical interactions.
There are different types of adsorbents, with the most common being clays, activated carbon and yeast cell walls. Their interlayer space, pores, and β-glucans represent their key adsorption factors, respectively (Jouany, 2007).
| To determine the effectiveness of mycotoxin adsorbents, in vitro tests are primarily used, allowing the evaluation of a large number of adsorbents and mycotoxins with the advantage of being comparable to in vivo tests. |
However, there are many variations of in vitro tests that have been developed over the years attempting to simulate the processes of the animals’ gastrointestinal tract.
The challenge with these approaches lies in the considerable variability observed in the adsorption results of mycotoxins.
| These protocols vary in complexity, ranging from a simple test with distilled water and incubation at room temperature (Lemek et al., 2001) to more complex methods that simulate the processes of the animal’s gastrointestinal tract using different pH values and including gastrointestinal enzymes, or using gastric juice as the incubation medium (Avantaggiato et al., 2004; Gallo and Masoero, 2010). |

Unfortunately, this diversity of experimental protocols has resulted in high variability in the results of the adsorption capacity of the adsorbents (Kihal et al., 2022).
COMPARATIVE DISCUSSION ON THE ADSORPTION CAPACITY OF ADSORBENTS BETWEEN IN VITRO AND IN VIVO STUDIES
Determining the adsorption capacity of mycotoxins in in vivo tests is essential to demonstrate the actual effectiveness of the product.
| In contrast to in vitro tests, in vivo tests replicate field conditions and the animal’s response to the supplementation of adsorbents in the presence of mycotoxins in diets. |
 To shed more light on the concordance of results from in vitro and in vivo studies, a network meta-analysis study was conducted on data published in the literature from studies that have evaluated the effectiveness of different adsorbents in reducing the concentration of aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) and its transfer from feed to milk after challenging dairy cows with AFB1 (Kihal et al., 2023).
To shed more light on the concordance of results from in vitro and in vivo studies, a network meta-analysis study was conducted on data published in the literature from studies that have evaluated the effectiveness of different adsorbents in reducing the concentration of aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) and its transfer from feed to milk after challenging dairy cows with AFB1 (Kihal et al., 2023).
The key finding of this study was the effectiveness of different sources of adsorbents [activated carbon (AC), bentonite, aluminosilicates, yeast cell wall, and a mixture of adsorbents (MIX)] significantly reduce the percentage of AFM1 in milk compared to the control.
![]() These results confirm the effectiveness of adsorbents in adsorbing aflatoxins from in vitro assays, although the adsorption percentage in vivo was lower. Additionally, the reduction percentage among different adsorbents in vivo did not differ, demonstrating a similar effect among the different adsorbents.
These results confirm the effectiveness of adsorbents in adsorbing aflatoxins from in vitro assays, although the adsorption percentage in vivo was lower. Additionally, the reduction percentage among different adsorbents in vivo did not differ, demonstrating a similar effect among the different adsorbents.
It is important to note that the number of in vivo studies was lower than the number of in vitro studies included in this meta-analysis (28 versus 68 articles).
![]() This difference may have an effect on the variability of the results, leading to high variability between treatment and comparisons.
This difference may have an effect on the variability of the results, leading to high variability between treatment and comparisons.
CHALLENGES AND LIMITATIONS OF IN VIVO STUDIES
In vivo studies, unlike in vitro tests, are complex, expensive and challenging to implement:
![]() They require the application of biosafety protocols for handling mycotoxins at the farm level.
They require the application of biosafety protocols for handling mycotoxins at the farm level. ![]() The required facilities are not available in most research centers.
The required facilities are not available in most research centers.
In addition, similar to in vitro tests, in vivo studies must be conducted under experimental conditions to avoid misleading results.

Defining the adsorbent-to-mycotoxin ratio is a common challenge in both in vitro and in vivo studies, as working with inappropriate proportions can either favor or unfavorably impact the mycotoxin adsorption results.
The method of contaminating the feed in experimental work is also a key factor in assessing adsorption capacity.
For example, supplementing naturally contaminated feed can affect the results compared to directly supplementing pure AFB1 into the cow’s rumen.
![]() This is because naturally contaminated feed may contain different types of aflatoxins (AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, or AFG2) or other mycotoxins, resulting in synergy or competition phenomena for binding to the tested adsorbent.
This is because naturally contaminated feed may contain different types of aflatoxins (AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, or AFG2) or other mycotoxins, resulting in synergy or competition phenomena for binding to the tested adsorbent.
The raw material used for fungal development is crucial, as fungi use nutrients from the contaminated grain for their growth, and using different types of grains can also affect fungal development and mycotoxin production.
| Nevertheless, in vivo experiments are the best method to test the effectiveness of adsorbents and allow for a deeper understanding of how the products function in animals. |

The review of results from in vitro and in vivo studies on adsorbents (Kihal et al., 2023) allowed confirming that their adsorption capacity for aflatoxins in vitro was similar to in vivo experiments where different adsorbents (activated carbon, bentonite, and aluminosilicates) unsuccessfully reduced AFM1 concentration in milk at a range of 26-45%.
In contrast, yeast cell wall exhibited the lowest adsorption in capacity in in vitro tests, which aligns with in vivo tests where it was the least effective adsorbent in reducing the transfer of AFM1 in milk.
![]() It is worth noting that the use of adsorbents in vivo resulted in a lower adsorption capacity compared to in vitro results, with a decrease of over 50% for activated carbon bentonite, and yeast cell wall, and a decrease of 67% for aluminosilicates.
It is worth noting that the use of adsorbents in vivo resulted in a lower adsorption capacity compared to in vitro results, with a decrease of over 50% for activated carbon bentonite, and yeast cell wall, and a decrease of 67% for aluminosilicates.
Cabe reseñar que el uso de los adsorbentes in vivo resultó en una menor capacidad de adsorción en comparación con los resultados in vitro, con una disminución de más del 50% para el CA, la bentonita y la LEV, y una disminución del 67% para HSCAS.
In this regard, it is suggested that under in vivo conditions, the gastrointestinal tract content (enzymes, nutrients, bacteria) interferes and competes with mycotoxins for adsorption sites on the adsorbents, leading to an overall decrease in capacity. This contrasts with in vitro conditions where incubation media contain fewer organic molecules.  |
WHAT IS THE POTENTIAL OF MYCOTOXIN ADSORBENTS TO INTERFERE WITH THE ADSORPTION OF OTHER NUTRIENTS, AND WHICH IS THE BEST TOOL TO VERIFY IT, IN VITRO OR IN VIVO?
Recent studies in our laboratory have shown that the adsorption capacity of mycotoxin adsorbents is affected by: →Adsorbent type → Mycotoxin type → The characteristics of the incubation medium.
(Kihal et al., 2022)
Furthermore, this capacity could be altered by the interaction of nutrients present in the same environment with mycotoxins, both in vivo and in vitro.
|
The adsorption mechanism of adsorbents is non-selective, as it not only binds to mycotoxins but can also adsorb other molecules found in the animal’s gastrointestinal tract, including nutrients. This ability to bind nutrients is attributed to the physicochemical similarities of some nutrients with mycotoxins that allow for their interaction. |
In vitro studies on the adsorption capacity of nutrients
The ability of adsorbents to adsorb nutrients has been studied using in vitro models.
|
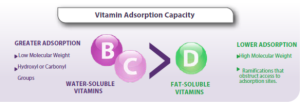
→ Kiah et al. (2020;2021) studied the interaction of six different adsorbents with amino acids and vitamins: The authors noted an adsorption range of 27-37% for amino acids, 25-58% for water-soluble vitamins, and 10-29% for fat-soluble vitamins. → Vekiru et al. (2007) also observed that activated carbon (CA) adsorbed a large proportion of vitamin B8 (78%) and B12 (99%), while bentonite had lower adsorption of vitamin B12 (47%). → Barrientos-Velázquez et al. (2016) reported that bentonite absorbed 34% of vitamin B1, and simultaneously, aflatoxin adsorption was reduced by 34%, indicating direct competition of other nutrients for adsorption sites. → Mortland et al. (1983) reported that smectite has the capacity to absorb vitamin B2 (50%). → It has also been observed that bentonite and montmorillonite adsorb proteins in an in vitro model (Ralla et al., 2010; Barrientos-Velázquez et al., 2016) → The ability of adsorbents to adsorb minerals was also investigated in vitro by Tomasevic-Canovic et al. (2001), who observed a high capacity of bentonite to adsorb copper (56%) and cobalt (73%), while the adsorption of zinc (12%) and manganese (12%) was relatively low. |

These results were mainly attributed to the physicochemical properties of each nutrient
![]() The adsorption capacity of water-soluble vitamins was higher due to their low molecular weight and the presence of more than one hydroxyl or carbonyl group, ensuring a stable adsorption with these adsorbents.
The adsorption capacity of water-soluble vitamins was higher due to their low molecular weight and the presence of more than one hydroxyl or carbonyl group, ensuring a stable adsorption with these adsorbents.
![]() The adsorption of vitamin D was lower due to its higher molecular weight and the presence of different branches that hinder its entry into the adsorbent’s adsorption sites.
The adsorption of vitamin D was lower due to its higher molecular weight and the presence of different branches that hinder its entry into the adsorbent’s adsorption sites.
Despite these results, there are technical challenges when applying these methods to some nutrients, as some of them are sensitive to environmental factors and may undergo alterations during incubation.
![]() Kiha et al. (2021) observed that vitamin A disappeared from the incubation medium after 4 hours of incubation, making its assessment unfeasible, while vitamins D and E were most stable during the degradation kinetics and showed more than 90% stability.
Kiha et al. (2021) observed that vitamin A disappeared from the incubation medium after 4 hours of incubation, making its assessment unfeasible, while vitamins D and E were most stable during the degradation kinetics and showed more than 90% stability.
![]() Díaz et al. (2004) pointed out that the results of in vitro tests should not be considered as final results and suggested that in vivo studies should be conducted to obtain more reliable outcomes.
Díaz et al. (2004) pointed out that the results of in vitro tests should not be considered as final results and suggested that in vivo studies should be conducted to obtain more reliable outcomes.
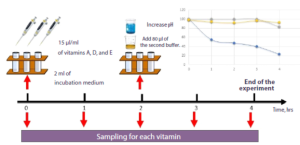
Figure 1. Assessment of the stability of fat-soluble vitamins in the incubation medium.

 In vivo studies on the adsorption capacity of nutrients
In vivo studies on the adsorption capacity of nutrients
The bioavailability of nutrients in presence of mycotoxin adsorbents has also been studied in vivo.
 Briggs and Fox (1956) observed that supplementing chicken diets with 2-3% bentonite resulted in a vitamin A deficiency.
Briggs and Fox (1956) observed that supplementing chicken diets with 2-3% bentonite resulted in a vitamin A deficiency.
 The zinc content also decreased in the bones of chickens after supplementation with 0.5% to 1% HSCAS in the diet (Chung et al., 1989).
The zinc content also decreased in the bones of chickens after supplementation with 0.5% to 1% HSCAS in the diet (Chung et al., 1989).
 On the other hand, Afriyie-Gyawu (2004) and Pimpukdee et al. (2004) observed that the inclusion of 0.5% bentonite did not affect the concentration of vitamin A in the liver, and Chung et al. (1989) found that the inclusion of HSCAS did not affect the bioavailability of vitamin A, vitamin B2 and manganese in chicks.
On the other hand, Afriyie-Gyawu (2004) and Pimpukdee et al. (2004) observed that the inclusion of 0.5% bentonite did not affect the concentration of vitamin A in the liver, and Chung et al. (1989) found that the inclusion of HSCAS did not affect the bioavailability of vitamin A, vitamin B2 and manganese in chicks.
 Sulzberger et al. (2016) and Kihal et al. (2022), after supplementing dairy cows with 1.2% and 2% montmorillonite in the diet, also did not observe changes in the plasma concentration of vitamins A,D,E, B1, and B6.
Sulzberger et al. (2016) and Kihal et al. (2022), after supplementing dairy cows with 1.2% and 2% montmorillonite in the diet, also did not observe changes in the plasma concentration of vitamins A,D,E, B1, and B6.

 Maki et al. (2016) supplemented HSCAS cows at 1.2% of dry matter of the diet and did not observe negative effects on the bioavailability of vitamins A and B2 in the milk.
Maki et al. (2016) supplemented HSCAS cows at 1.2% of dry matter of the diet and did not observe negative effects on the bioavailability of vitamins A and B2 in the milk.
RECOMMENDATIONS TO IMPROVE THE ACCURACY OF IN VITRO AND IN VIVO TESTS
Standardized proportions of adsorbent to mycotoxin
In addition to factors limiting specific interaction between adsorbents and mycotoxins, the adsorption mechanism of adsorbents is saturable and depends on the number of adsorption sites available of mycotoxins in the matrix.
For this reason, the adsorbent-to-mycotoxin ratio is an essential factor in in vitro tests, where the adsorption capacity can be easily manipulated.
![]() High adsorbent concentration and low mycotoxin concentration: incubating a high concentration of adsorbent with a low concentration of mycotoxins will result in a higher adsorption capacity of the tested adsorbents because there are more adsorption sites available than mycotoxins present in the medium.
High adsorbent concentration and low mycotoxin concentration: incubating a high concentration of adsorbent with a low concentration of mycotoxins will result in a higher adsorption capacity of the tested adsorbents because there are more adsorption sites available than mycotoxins present in the medium.
![]() Low adsorbent concentration and high mycotoxin concentration: incubating a low concentration of adsorbent with a high concentration of mycotoxins will result in a lower adsorption capacity due to the saturation of available adsorption sites on the adsorbents.
Low adsorbent concentration and high mycotoxin concentration: incubating a low concentration of adsorbent with a high concentration of mycotoxins will result in a lower adsorption capacity due to the saturation of available adsorption sites on the adsorbents.
(Sulzberger et al., 2017)
| Using the selected data for the in vitro adsorbent efficacy analysis, the adsorbent-to-mycotoxin ratios employed in current techniques resulted in a broad range of ratios, regardless of the type of mycotoxin adsorbent. (1:0,00007 a 1:600 mg/μg, Table 1) |
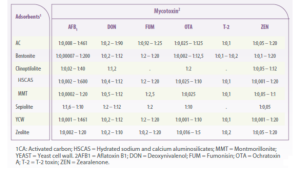
Table 1. Ranges of mycotoxin adsorbent to mycotoxin ratio (mg:μg) used in in vitro tests to determine the adsorption capacity of different mycotoxins and mycotoxin adsorbents.
It is important to establish a standardized adsorbent-to-mycotoxin ratio to be used in in vitro tests to ensure fair comparisons.
→EFSA (2017) considers adsorbents to be safe and establishes high safety limits (20 kg/t of feed)
The currently recommended doses of adsorbents are generally established by the marketing companies of the adsorbents, which conduct in vitro tests using different inclusion doses of adsorbents.
![]() The required dose varies depending on the type of adsorbent, altering its chemical properties with the chemical composition and nature of the adsorbent. However, it should be possible to recommend a range of proportions to be followed during in vitro experiments.
The required dose varies depending on the type of adsorbent, altering its chemical properties with the chemical composition and nature of the adsorbent. However, it should be possible to recommend a range of proportions to be followed during in vitro experiments.
 Díaz et al. (2004) recommended a concentration of 1.2% of dairy dry matter of adsorbent, equivalent to 300 g/day/cow. However, the daily intake of mycotoxins is highly variable and depends on the type of mycotoxin.
Díaz et al. (2004) recommended a concentration of 1.2% of dairy dry matter of adsorbent, equivalent to 300 g/day/cow. However, the daily intake of mycotoxins is highly variable and depends on the type of mycotoxin.
Therefore, it is reasonable to propose an appropriate dose related to the minimum toxic levels of each mycotoxin evaluated by the European Commission (EC, 2006 on raw materials)
To standardize an in vitro protocol, we propose using an adsorbent-to-mycotoxin ratio close to that found under field conditions.
![]() With this goal in mind, the daily intake of adsorbents and mycotoxins should be determined.
With this goal in mind, the daily intake of adsorbents and mycotoxins should be determined.
![]() The practical dose of adsorbents should be considered based on what has been demonstrated to be effective in adsorbing mycotoxins.
The practical dose of adsorbents should be considered based on what has been demonstrated to be effective in adsorbing mycotoxins.
Because mycotoxicosis occurs in animals with high concentration of mycotoxins, we propose using the minimum toxic concentration for each mycotoxin multiplied by 10 for in vitro tests.
Thus, the daily intake will be 10 times higher than the minimum toxic limits, considering an average consumption for each animal species.
This adsorbent-to-mycotoxin ratio (mg/μg) should allow for the evaluation of the adsorbents’ capacity to adsorb toxic levels of mycotoxins in an appropriate proportion.
Standardization of in vitro tests
A standardized procedure should also consider other aspects, such as the characteristics and volume of the incubation media, duration and pH, among other factors.
Validation process of in vitro tests
Finally, like any in vitro test, validation would be necessary.
However, conducting in vivo tests to provide sufficient data for each adsorbent and each mycotoxin for the validation process, is very challenging. This increases the difficulty of developing a reliable and validated test.
CONCLUSIONS
Due to the variability in the results and the limited available data, it is important to:
Validate the results with in vivo tests. Actual in vitro protocols used to evaluate adsorbents are designed as detection method, mainly employed during product development because they provide quick and cost-effective information about product efficacy. ⇒However, this information is limited due to the high variability between methods and laboratories. |
The current challenge is to develop a new validated method that provides reliable results for different adsorbents and mycotoxins.
![]() A validated method can also be used as a refinement procedure to replace costly and complicated in vivo studies.
A validated method can also be used as a refinement procedure to replace costly and complicated in vivo studies.