Fierro JA1, Lara J1, Zúñiga R1, Montalvo O1, Rosas S1, Medina JC1 y Rodríguez E2.
1NUTEK S.A. de C.V. 2 Applied research S.A. de C.V.
INTRODUCTION
 T-2 toxin is a trichothecene primarily produced by Fusarium sporotrichioides, which causes reduced feed intake and weight gain, oral lesions, and necrosis of lymphoid tissues and the oral mucosa in birds (Morehouse, 1985).
T-2 toxin is a trichothecene primarily produced by Fusarium sporotrichioides, which causes reduced feed intake and weight gain, oral lesions, and necrosis of lymphoid tissues and the oral mucosa in birds (Morehouse, 1985).
 T-2 toxin causes significant losses in the livestock sector (CAST 2003), which is why the use of antimycotoxin additives is of great importance. However, the reduction in the bioavailability of T-2 toxin is limited in current products. Various treatments have been developed to improve this characteristic, but these experimental materials need to be evaluated. T-2 toxin causes significant losses in the livestock sector (CAST 2003), which is why the use of antimycotoxin additives is of great importance. However, the reduction in the bioavailability of T-2 toxin is limited in current products. Various treatments have been developed to improve this characteristic, but these experimental materials need to be evaluated. |

OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the protective effect of an experimental organoaluminosilicate adsorbent against the adverse effects of 1,800 ppb of T-2 toxin in broiler chickens during the growing phase (days 1 to 28 of age).
MATERIALS & METHODS
A total of 84 male broiler chickens of the Ross commercial line, one day old, were randomly distributed into 3 treatments of 7 birds with 4 replicates. They were provided with controlled feed and water ad libitum for 28 days.
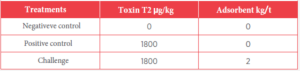
Table 1. Experimental diets.
The birds were weighed on day one, and their individual weight was recorded weekly until the end of the experiment. They were vaccinated on day 10 against Newcastle disease. The animals were bled and sacrificed, organs were removed and individually weighed to determine their relative weight, and samples were taken for histopathological tests.
 Complete blood samples were used to perform a complete blood count, and from the serum, the concentrations of xanthophylls, vitamin A, and HI for Newcastle were quantified. The left tibias were removed and analyzed for ash, phosphorus, calcium, manganese, and zinc. Complete blood samples were used to perform a complete blood count, and from the serum, the concentrations of xanthophylls, vitamin A, and HI for Newcastle were quantified. The left tibias were removed and analyzed for ash, phosphorus, calcium, manganese, and zinc. |
The data obtained were analyzed by ANOVA using the SYSTAT statistical program, with Tukey’s test to define differences between means. The significance level was set at 0.05 probability.

RESULTS
 The results at 14, 21, and 28 days of age showed statistically significant differences between the treatments in weight gain and feed conversion.
The results at 14, 21, and 28 days of age showed statistically significant differences between the treatments in weight gain and feed conversion.
The product’s effectiveness based on weight gain was 74.6%. In terms of feed intake, there were no statistically significant differences; however, the standard error was lower in the challenge treatment.
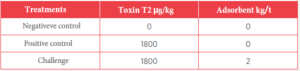
Table 2. Productive parameters. Means with different letters are statistically significant at (p < 0.05).
![]() The white blood cell and lymphocyte counts in whole blood and the concentrations of vitamin A and xanthophylls in serum showed statistically significant differences.
The white blood cell and lymphocyte counts in whole blood and the concentrations of vitamin A and xanthophylls in serum showed statistically significant differences.
![]() Furthermore, chickens treated with the adsorbent and toxin showed a better vaccination response, according to the results of the HI test for Newcastle disease.
Furthermore, chickens treated with the adsorbent and toxin showed a better vaccination response, according to the results of the HI test for Newcastle disease.
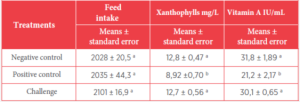
Table 3. Means with different letters are statistically significant at (p < 0.05).

Effect on pigmentation
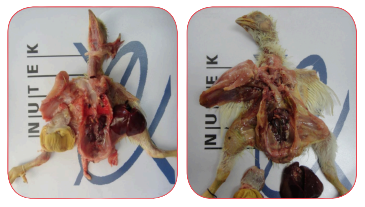
7 and 14 days of contaminated feed consumption, effect on the gizzard.
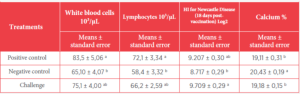
Table 4. Means with different letters are statistically significant at (p < 0.05).
Intestinal integrity was affected, mainly in the duodenum and slightly in the jejunum. In the histopathological analyses, the birds in the mycotoxin group showed lesions in the tongue, larynx, proventriculus, gizzard, liver, and kidneys. The following table presents the lesion score in the oral cavity.
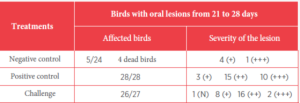
Table 5.
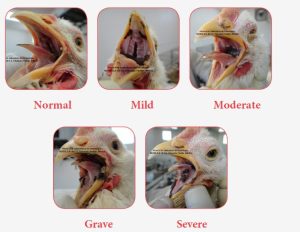
DISCUSSION & CONCLUSIONS
Mycotoxin adsorbents must be evaluated “in vivo“ to demonstrate their effectiveness; moreover, they must protect target organs and animal systems (reduce productive performance and immune response).
 The inclusion of the adsorbent in the contaminated diet statistically improved animal weight and proved effective in preventing the toxic effects of T-2 toxin in broiler chickens. The inclusion of the adsorbent in the contaminated diet statistically improved animal weight and proved effective in preventing the toxic effects of T-2 toxin in broiler chickens. |
REFERENCES
Council for Agricultural Science and Technology. 2003. Ames, Iowa, USA. No. 139. Morehouse LG.1985. Mycotoxins of veterinary importance in the United States. 383- 410.