The Importance of Minerals for Dogs and Cats and Their Effects During Extrusion Process and Shelf Life
For a diet to be deemed complete and balanced, it needs to encompass all the essential nutrients necessary to fulfill the unique nutritional requirements of each species.
The formulation of foods involves ingredients that supply all essential nutrients, categorized into groups:
Macronutrients comprise proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and fibers;
Micronutrients are represented by minerals and vitamins.
Moreover, a food may contain ingredients in its formulation with functional properties, providing additional benefits to the animals.
 From a nutritional standpoint, minerals are essential inorganic elements for the development and maintenance of the organism.
From a nutritional standpoint, minerals are essential inorganic elements for the development and maintenance of the organism.
Minerals can be categorized according to their biological role and/or content found in animal tissues, playing numerous crucial roles in the organism, such as: [register]
 According to necessity, minerals are divided into macroelements and microelements. Macroelements are required by the animal body in larger quantities, while microelements are needed in smaller amounts.
According to necessity, minerals are divided into macroelements and microelements. Macroelements are required by the animal body in larger quantities, while microelements are needed in smaller amounts.
 These minerals can be found in various foods, both of animal and plant origin, with each serving a specific function contributing to the body’s balance.
These minerals can be found in various foods, both of animal and plant origin, with each serving a specific function contributing to the body’s balance.
In the context of Pet Food, it’s crucial to consider the quality and sources of minerals to determine the amount available for absorption and utilization, in other words, their bioavailability.
 Mineral bioavailability refers to the quantity of a mineral present in a specific chemical form that is available for absorption and utilization by the body.
Mineral bioavailability refers to the quantity of a mineral present in a specific chemical form that is available for absorption and utilization by the body.
This process is influenced by various factors, including the rate of intestinal absorption, which depends on elements such as the mineral content, food matrix, interaction with other nutrients, chemical form, and processing.
There are discrepancies regarding the availability of minerals in organic and inorganic forms, especially in the case of trace minerals like Mercury, Lead, Cadmium, and Arsenic.
The response to this availability is influenced by the specific mineral, dietary conditions, and the physiological state of the animal.

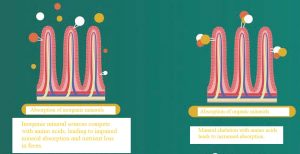
Figure 1. Intestinal absorption of inorganic and organic minerals.
 Research indicates that mineral bioavailability can be enhanced when they are bound to organic molecules, such as amino acids or peptides, resulting in the designation of organic or chelated minerals.
Research indicates that mineral bioavailability can be enhanced when they are bound to organic molecules, such as amino acids or peptides, resulting in the designation of organic or chelated minerals.
Chelated minerals have been extensively studied due to their higher bioavailability compared to inorganic sources.
| The processing of ingredients or food can also affect the bioavailability of minerals. |
Excessive heat treatment can reduce the bioavailability of certain minerals, and interaction with other ingredients in the formulation can interfere with mineral absorption.
 Furthermore, the balance between different minerals in the diet also influences their bioavailability, as an excess of one mineral can inhibit the absorption of another.
Furthermore, the balance between different minerals in the diet also influences their bioavailability, as an excess of one mineral can inhibit the absorption of another.

This phenomenon was evidenced in a study conducted by Silva (2021), in which different sources (inorganic vs. organic) and levels (1x and 2x the FEDIAF recommendation, 2021) of minerals were tested.




| Additionally, it’s important to provide minerals in easily absorbable forms and quantities, taking into account process variables to minimize adverse effects during the manufacturing and shelf life of Pet Food. |
Bibliographical references available upon request [/register]
You may also like to read: “Ensuring Food Safety in Natural Diets for Dogs & Cats through Freezing methods”