Agricultural residues represent a potential alternative for mycotoxin decontamination in animal feed.
A deficiency such as the presence of mycotoxins in animal feed, can cause significant economic losses in animal production systems. Taking this into consideration, the poultry industry can suffer significant impacts due to these toxins.
The study of organic adsorbents which are safe, cost-effective and effective, has drawn great interest in recent years.
There are numerous organic adsorbents (plant fibers, yeast cell wall extracts and bacteria)which have evidenced potential mycotoxin adsorption efficacy (in vitro and in vivo). However, very few of these have been investigated under in vivo models.
Besides adsorbing mycotoxins, they can simultaneously adsorb micronutrients from the diet, with the potential risk of releasing toxic components, such as heavy metals or dioxins.
 For such reasons, in recent years, the study of organic adsorbents which are safe, cost-effective and effective, has drawn great interest.
For such reasons, in recent years, the study of organic adsorbents which are safe, cost-effective and effective, has drawn great interest.
Bio-adsorption technology is considered an optimal and sustainable alternative due to the fact that various materials can be used. Including:
![]() Agricultural waste: straw, nut shells, hazelnuts, almonds and coconuts, fruit seeds and pulp, corn potholes, peas, etc.,
Agricultural waste: straw, nut shells, hazelnuts, almonds and coconuts, fruit seeds and pulp, corn potholes, peas, etc.,
![]()
Micronized fibers that can be obtained from various plant materials such as wheat, barley, alfalfa, oats, and pea husks, among others.

These materials are characterized by: high efficiency for the removal of certain mycotoxins, low costs, low inclusion levels, as well as preventing nutritional value reductions within the diet.
 RESEARCH ON GRAPE POMACE AS A BIOADSORBENT
RESEARCH ON GRAPE POMACE AS A BIOADSORBENT
Avantaggiato et al. (2014), used grape pomace (peel and pulp) as a multimycotoxin bioadsorbent in an in vitro model.
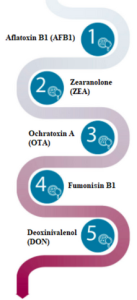
As por of their study, they used a mycotoxin mixture composed of:
![]() Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)
![]() Zearalenone (ZEA)
Zearalenone (ZEA)
![]() Ochratoxin A (OTA)
Ochratoxin A (OTA)
![]() Fumonisin B1 (FB1)
Fumonisin B1 (FB1)
![]() Deoxinivalenol (DON)
Deoxinivalenol (DON)
*At a concentration of 1 μg/mL of each toxin

Mycotoxin adsorption experiments were performed at a temperature of 37 °C and various parameters were evaluated such as: the effect of particle size, contact time between the bioadsorbent and mycotoxins, pH of the medium and bioadsorbent dose.
Mycotoxin adsorption was reported to gradually increase with decreasing particle size (<500 um);
![]() However, the five different particle sizes evaluated adsorbed significant amounts of AFB1, ZEA, OTA and FB1, while the adsorption of DON was negligible.
However, the five different particle sizes evaluated adsorbed significant amounts of AFB1, ZEA, OTA and FB1, while the adsorption of DON was negligible.
![]() The maximum adsorption values recorded for AFB1, ZEN, OTA and FB1 were 82%, 70%, 61% and 28%, respectively.
The maximum adsorption values recorded for AFB1, ZEN, OTA and FB1 were 82%, 70%, 61% and 28%, respectively.
The trial which evaluated the effect of contact time between the bioadsorbent and the mycotoxins had a duration of 2 h.
![]() In the initial stages of contact the adsorption of AFB1, ZEA, OTA and FB1, was fast, but it then became slower as it reached an equilibrium.
In the initial stages of contact the adsorption of AFB1, ZEA, OTA and FB1, was fast, but it then became slower as it reached an equilibrium.
![]() 50% of adsorption occurred during the first 3 min and maximum adsorption was achieved at 15 min.
50% of adsorption occurred during the first 3 min and maximum adsorption was achieved at 15 min.
![]() The adsorption of mycotoxins was highly dependent on pH; regarding the adsorption of AFB1 and ZEA, it was observed that the adsorption potential of the bioadsorbent was stable despite pH variations(from 3 to 9);
The adsorption of mycotoxins was highly dependent on pH; regarding the adsorption of AFB1 and ZEA, it was observed that the adsorption potential of the bioadsorbent was stable despite pH variations(from 3 to 9);
![]() However, the change in pH affected the adsorption of OTA and FB1.
However, the change in pH affected the adsorption of OTA and FB1.
 Overall, mycotoxin adsorption was significantly affected by the bioadsorbent dose. As the dose increased, the adsorption of mycotoxins was significantly higher for all cases.
Overall, mycotoxin adsorption was significantly affected by the bioadsorbent dose. As the dose increased, the adsorption of mycotoxins was significantly higher for all cases.
Greco et al. (2019), conducted an in vitro study with 51 agricultural by-products, in order to test them as mycotoxin bioadsorbents (AFB1, ZEA, OTA and FB1). They used a concentration of 1 μg/mL per toxin.
Some of the by-products tested were:
![]() Lentils,
Lentils,
![]() Chickpeas,
Chickpeas,
![]() Beans,
Beans,
![]() Onion leaves and cauliflower
Onion leaves and cauliflower
![]() Broccoli stalks,
Broccoli stalks,
![]() Asparagus and celery,
Asparagus and celery,
![]() Onion and fennel bulbs
Onion and fennel bulbs
![]() Bean, potato and tomato skin,
Bean, potato and tomato skin,
![]() Almond shell,
Almond shell,
![]() Artichoke residues,
Artichoke residues,
![]() Grape pomace,
Grape pomace,
![]() Orange and lemon residues,
Orange and lemon residues,
![]() Pomegranate seeds,
Pomegranate seeds,
![]() Banana peel, etc.
Banana peel, etc.
Of the 51 by-products, three were selected as promising mycotoxin bioadsorbents (grape pomace, artichoke residues and almond shells). These presented high levels of lignin and polyphenols.

From these three, the adsorption effectiveness for the following mycotoxins was highlighted:
![]() For AFB1, ZEA and OTA, their adsorption was not affected by the pH of the medium (7 and 3), However, adsorption was affected by the pH of the medium for FB1, which was absorbed to a lesser extent.
For AFB1, ZEA and OTA, their adsorption was not affected by the pH of the medium (7 and 3), However, adsorption was affected by the pH of the medium for FB1, which was absorbed to a lesser extent.
![]() The mycotoxin which was not adsorbed by the tested by-products was DON.
The mycotoxin which was not adsorbed by the tested by-products was DON.
![]() The highest percentage of adsorption occurred at a pH of 7 with the following values:
The highest percentage of adsorption occurred at a pH of 7 with the following values:
![]() Grape pomace: AFB1 (94%), ZEA (84%), OTA (80%) and FB1 (35%);
Grape pomace: AFB1 (94%), ZEA (84%), OTA (80%) and FB1 (35%);
![]() Artichoke residues: AFB1 (55%), ZEA (89%), OTA (3%) and FB1 (1%) and;
Artichoke residues: AFB1 (55%), ZEA (89%), OTA (3%) and FB1 (1%) and;
![]() Almond shell: AFB1 (87%), ZEA (76%), OTA (18%) and FB1 (20%).
Almond shell: AFB1 (87%), ZEA (76%), OTA (18%) and FB1 (20%).

 The efficacy of grape pomace overall, was associated with the presence of micronized fibers and phenolic compounds.
The efficacy of grape pomace overall, was associated with the presence of micronized fibers and phenolic compounds.
Fernandes et al. (2019), conducted an in vitro study with olive pomace and grape stems (20 mg/mL) as bioadsorbents for AFB1, OTA and ZEA.

High adsorption percentages were achieved for all the pH values tested (2, 5, 7 and 8),:
![]() AFB1 (olive pomace, 74%; grape stalks, 96%),
AFB1 (olive pomace, 74%; grape stalks, 96%),
![]() ZEA (olive pomace, 93 %; grape stalks, 99%),
ZEA (olive pomace, 93 %; grape stalks, 99%),
![]() However, OTA was the mycotoxin that presented the lowest adsorption percentage at a high pH. Nonetheless it adsorbed well at a pH of 2.
However, OTA was the mycotoxin that presented the lowest adsorption percentage at a high pH. Nonetheless it adsorbed well at a pH of 2.

Shar et al. (2016), used banana peel (60 mg/mL) as a novel mycotoxin bioadsorbent: aflatoxins (AFB1, AFB2, AFG1 and AFG2) and OTA. With concentrations of 0.5 μg/mL for each toxin.
![]() The adsorption capacity of banana peel increased with a increase in pH.
The adsorption capacity of banana peel increased with a increase in pH.
![]() The lowest percentage of aflatoxin adsorption occured at a of pH 3 with 24.9% and the maximum was at a pH of 9 with 74.6% for AFB1.
The lowest percentage of aflatoxin adsorption occured at a of pH 3 with 24.9% and the maximum was at a pH of 9 with 74.6% for AFB1.
![]() OTA was not adsorbed under any pH value.
OTA was not adsorbed under any pH value.

Adunphatcharaphon et al. (2020), evaluated the adsorption capacity of the durian shell (Durio zibthinus) at 0.5% (w / v).
![]() Durian husk was treated with acid to improve adsorption against AFB1, OTA, ZEA, DON and FB1.
Durian husk was treated with acid to improve adsorption against AFB1, OTA, ZEA, DON and FB1.
![]() Which were included in a solution containing 1 μg/mL of each toxin
Which were included in a solution containing 1 μg/mL of each toxin
![]() EMploying an in vitro model which simulated certain conditions of the GI tract.
EMploying an in vitro model which simulated certain conditions of the GI tract.
![]() The authors reported that the acid-treated shell exhibited the highest mycotoxin adsorption capacity: AFB1 (98.4%), ZEA (98.4%), OTA (97.3%), FB1 (86.1%) and; DON (2%).
The authors reported that the acid-treated shell exhibited the highest mycotoxin adsorption capacity: AFB1 (98.4%), ZEA (98.4%), OTA (97.3%), FB1 (86.1%) and; DON (2%).

Our research group conducted a study using a diet contaminated with AFB1 (100 μg AFB1/kg), to which three different 1.5% (w/w) bioadsorbents were added:
 Banana peel
Banana peel
 Hawthorn leaves(Pyracantha koidzumii)
Hawthorn leaves(Pyracantha koidzumii)
 Aloe vera powder
Aloe vera powder
To adsorb AFB1 in an in vitro model, which simulates the GIT conditions of birds.
![]() Zavala-Franco et al. (2018) reported that, the highest adsorption value for AFB1 occured at a pH of 7 with 69%, 46% and 28% for aloe, Pyracantha leaves and banana peel, respectively.
Zavala-Franco et al. (2018) reported that, the highest adsorption value for AFB1 occured at a pH of 7 with 69%, 46% and 28% for aloe, Pyracantha leaves and banana peel, respectively.

![]() It is attributed that the adsorption of AFB1 was carried out due to the presence of numerous functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amide, phosphate and ketone.
It is attributed that the adsorption of AFB1 was carried out due to the presence of numerous functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amide, phosphate and ketone.
Other work carried out by our research team focused on studying the adsorption potential of firethorn (Pyracantha koidzumii), against aflatoxins (AFB1 and AFB2) at a concentration of 100 ng/mL.
Ramales-Valderrama et al. (2016), used the leaves and berries of this plant at 0.5% (w / v). The obtained results were:
![]() The highest adsorption percentages were 86% and 82% using leaves and leaves + berries, respectively.
The highest adsorption percentages were 86% and 82% using leaves and leaves + berries, respectively.
![]() When the berries were used, AFB1 adsorption was significantly lower (46%).
When the berries were used, AFB1 adsorption was significantly lower (46%).
 It is interpreted that the adsorption of AFB1 is carried out by the interaction between the AFB1 molecule and the functional groups present in the bioadsorbent (hydroxyl, amino, carboxyl and carbonyl).
It is interpreted that the adsorption of AFB1 is carried out by the interaction between the AFB1 molecule and the functional groups present in the bioadsorbent (hydroxyl, amino, carboxyl and carbonyl).

Recently,our group conducted in vitro studies using lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. ), horsetail (Equisetum arvense L. ), and firethorn leaves(Pyracantha koidzumii) at low inclusion levels(0.1% and 0.5% w/v) against AFB1 adsorption (190 ng/mL) They employed a model which simulated certain conditions of birds’ gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
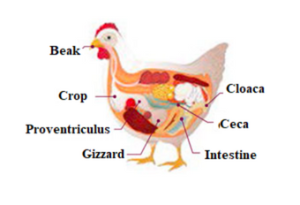
![]() Nava-Ramírez et al. (2021), reported that a lettuce-based bioadsorbent at an inclusion level of 0.1%, at a pH of 7 had the best AFB1 adsorption percentage (95%), compared to horsetail (71%) and firethorn (63%).
Nava-Ramírez et al. (2021), reported that a lettuce-based bioadsorbent at an inclusion level of 0.1%, at a pH of 7 had the best AFB1 adsorption percentage (95%), compared to horsetail (71%) and firethorn (63%).
![]() It is attributed that the adsorption of AFB1 by lettuce, is based on a set of interactions between the AFB1 molecule and the bioadsorbent through physicochemical interactions. Such as electrostatic, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonds and the formation of AFB1-chlorophyll complexes.
It is attributed that the adsorption of AFB1 by lettuce, is based on a set of interactions between the AFB1 molecule and the bioadsorbent through physicochemical interactions. Such as electrostatic, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonds and the formation of AFB1-chlorophyll complexes.

The most recent work carried out by our research group was based on the use of two bioadsorbents prepared organically from kale residues (Brassica oleracea L. ) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. ).
Vázquez-Durán et al. (2021), used a dynamic in vitro model that simulated the GIT conditions of birds;
![]() Bioadsorbents were used at 0.5% (w/w) in a diet contaminated with AFB1 (100 μg AFB1/kg).
Bioadsorbents were used at 0.5% (w/w) in a diet contaminated with AFB1 (100 μg AFB1/kg).
![]()
The bioadsorbent prepared from kale had an adsorption percentage of 93.6% and that of lettuce was 83.7%.
It was elucidated that, if the bioadsorbents contain a high number of hydrophobic groups (methyl and aromatic), as is the case of kale, the elimination of AFB1 is more efficient.

![]() In addition, it was shown that chlorophyll has the ability to form AFB1-chlorophyll complexes, so a high chlorophyll content in bioadsorbents will significantly improve AFB1 adsorption.
In addition, it was shown that chlorophyll has the ability to form AFB1-chlorophyll complexes, so a high chlorophyll content in bioadsorbents will significantly improve AFB1 adsorption.
![]() Taking these results into account, it can be concluded that agricultural by-products represent effective and low-cost mycotoxin adsorbent alternatives when compared to inorganic adsorbents.
Taking these results into account, it can be concluded that agricultural by-products represent effective and low-cost mycotoxin adsorbent alternatives when compared to inorganic adsorbents.
![]() Bioadsorbents have significant mycotoxin adsorption potential in in vitro models that simulate bird GIT conditions (exhibiting significant efficacy levels over a wide range of pH values and temperatures).
Bioadsorbents have significant mycotoxin adsorption potential in in vitro models that simulate bird GIT conditions (exhibiting significant efficacy levels over a wide range of pH values and temperatures).
![]() Bioadsorbents are mainly made up of cellulose, lignin, hemicellulose, pectin, lipids, amongst other compounds. These are rich in different functional groups which are capable of binding with mycotoxins.
Bioadsorbents are mainly made up of cellulose, lignin, hemicellulose, pectin, lipids, amongst other compounds. These are rich in different functional groups which are capable of binding with mycotoxins.
![]() The outstanding capacity for binding mycotoxins which is attributed to biosorbents, is based on a set of interactions between mycotoxins and these organic by-products. Including physicochemical interactions such as electrostatics, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonds and the formation of AFB1-chlorophyll complexes.
The outstanding capacity for binding mycotoxins which is attributed to biosorbents, is based on a set of interactions between mycotoxins and these organic by-products. Including physicochemical interactions such as electrostatics, π–π interactions, hydrogen bonds and the formation of AFB1-chlorophyll complexes.
